Circular coding

The mating faces of circular connectors are coded to prevent mismating. The coding is incorporated into the inner shape of the insulation bodies. M8 and M12 circular connectors have codings that visually resemble letters used to distinguish the coding and the corresponding application. Discover the coding for all circular connector types.
A-coded
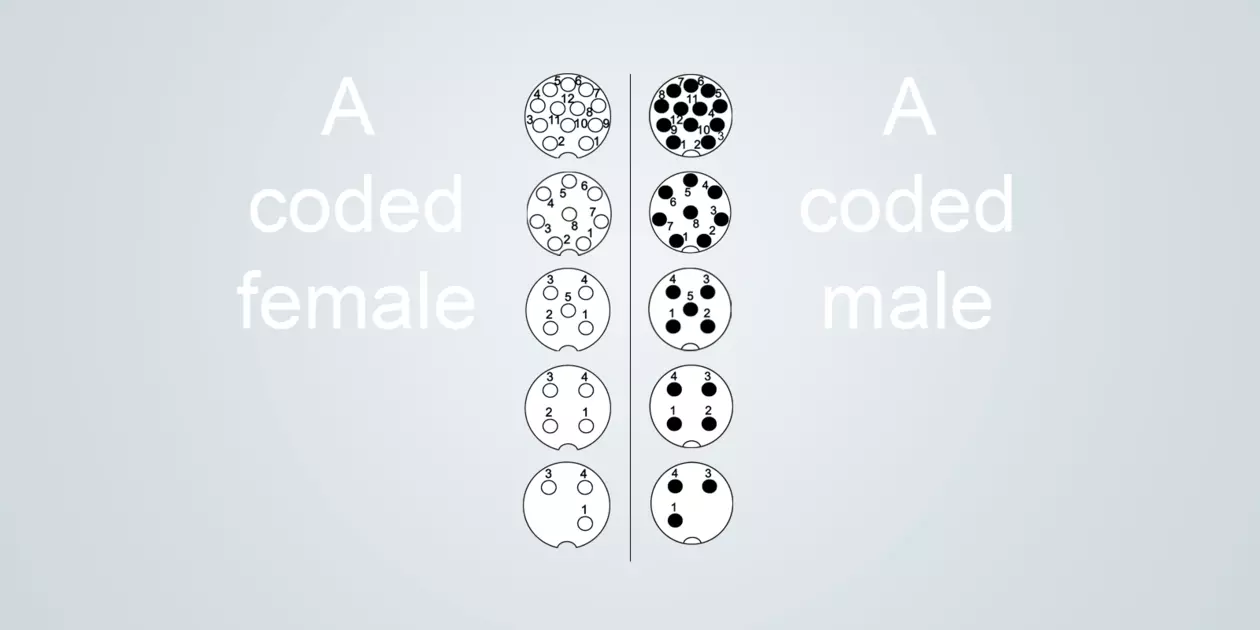
Typical application: Transmission of signals for sensors and actuators
Sizes M8 (IEC 61076-2-104) and M12 (IEC 61076-2-101)
Rated current 1.5 – 7.5 A
Rated voltage 30 - 250 V
Number of contacts 3 - 12
The A-coding in 3 – 5 poles is used for the power supply of field devices. The 8 –12 pole A-coding is a typical coding for transmitting signals.
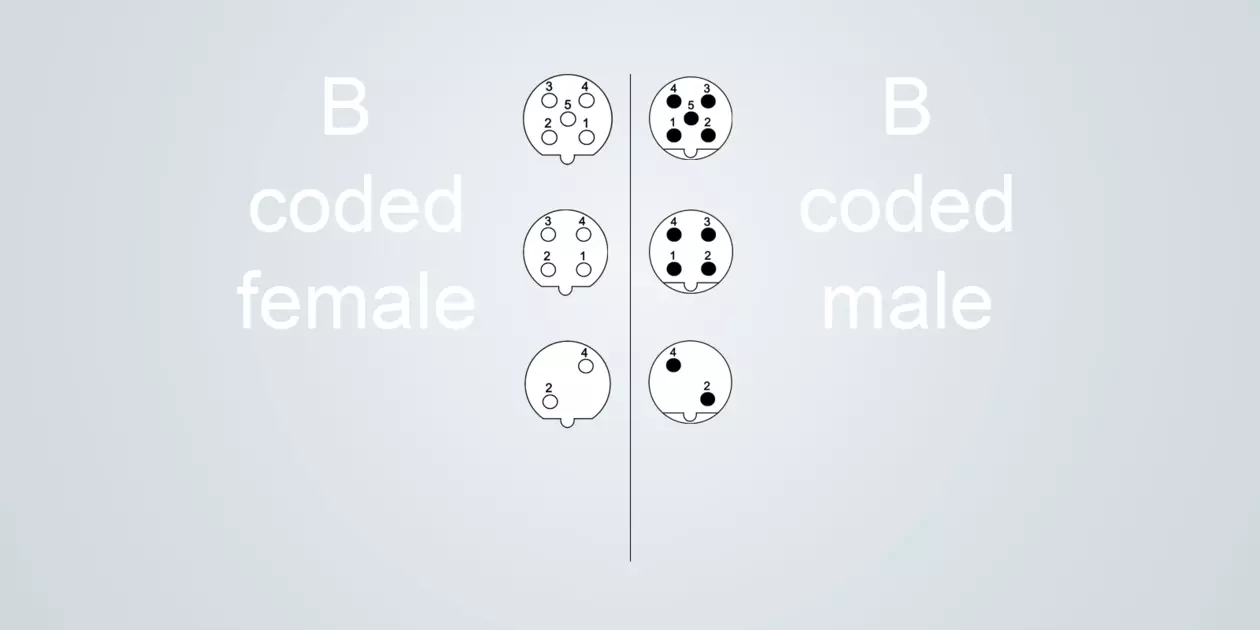
B-coded
Typical application: Data transmission for fieldbus systems (PROFIBUS)
Size M12 (IEC 61076-2-101)
2, 4 and 5 poles
The B-coding is used for PROFIBUS transmissions.
D-coded
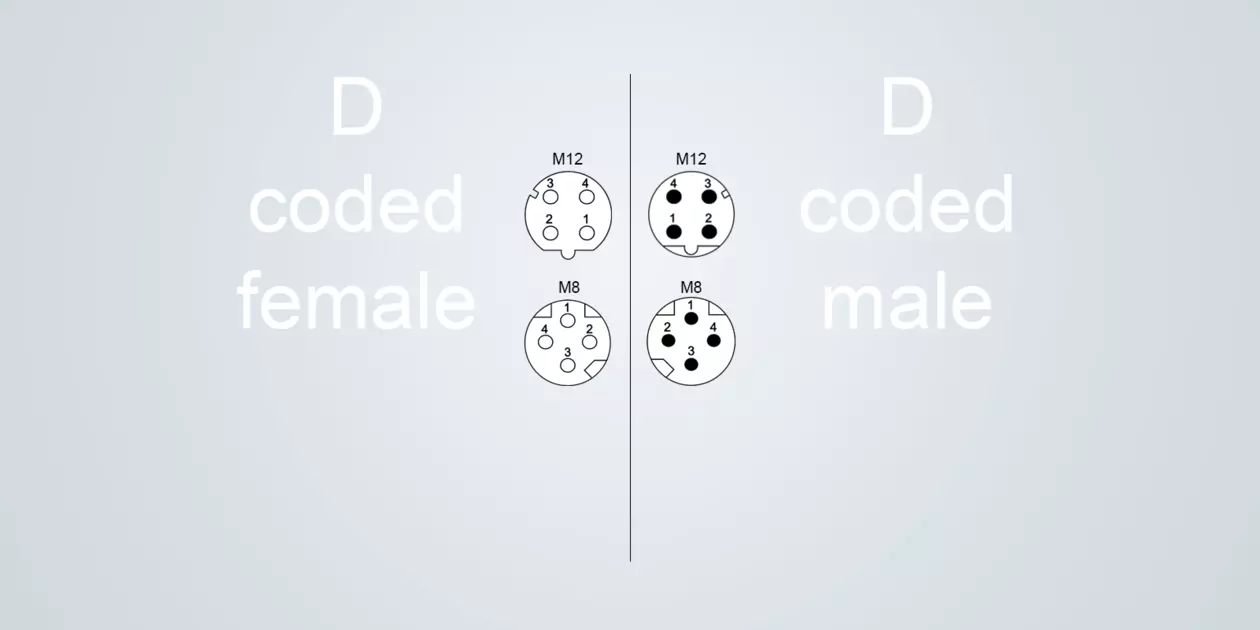
Typical application: Data transmission for Industrial Ethernet networks
Size M12 (IEC 61076-2-101), M8 (IEC 61076-2-114)
Data rate 100 Mbit/s
D-coding is used in circular connectors for transmitting data for Industrial Ethernet applications. D-coding is specified for data rates up to 100Mbit/s Fast Ethernet.
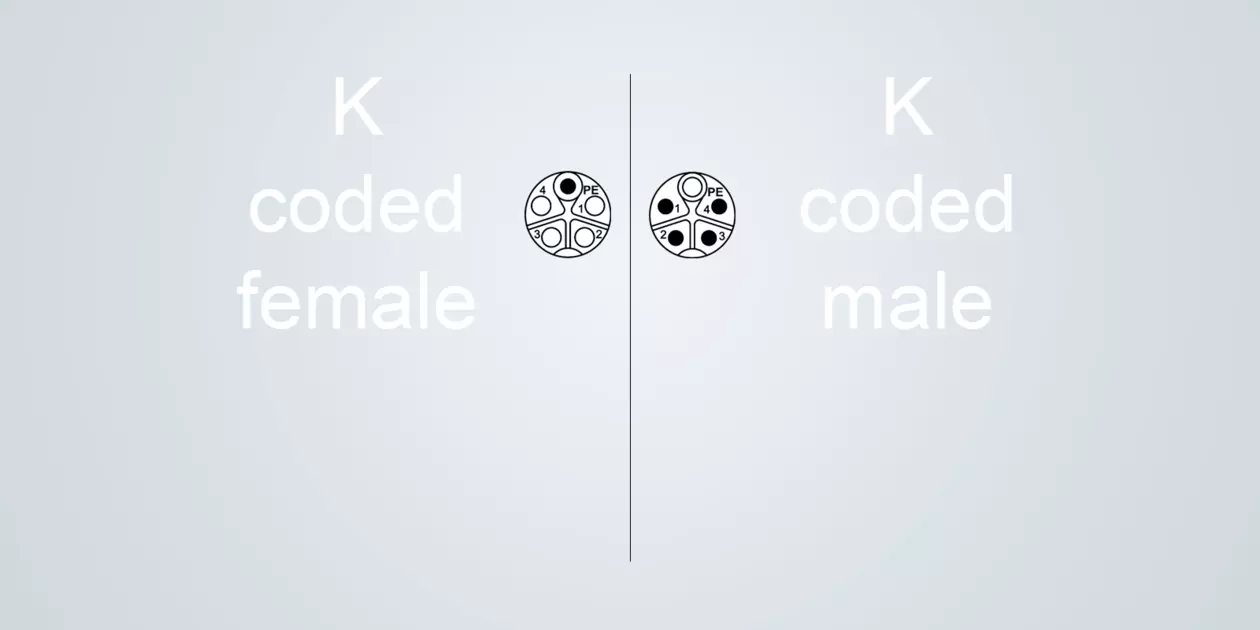
K-coded
Typical application: Power transmission of small drives
Size M12 (IEC 61076-2-111)
Electricity / voltage 12 A / 630 V
4 poles + PE
K-coding is one of the codings used for transmitting power. M12 circular connectors in K-coding are typically used for drives up to 7.5 kW. M12 Power is a space-saving solution that can be used to supply power to other devices.
L-coded
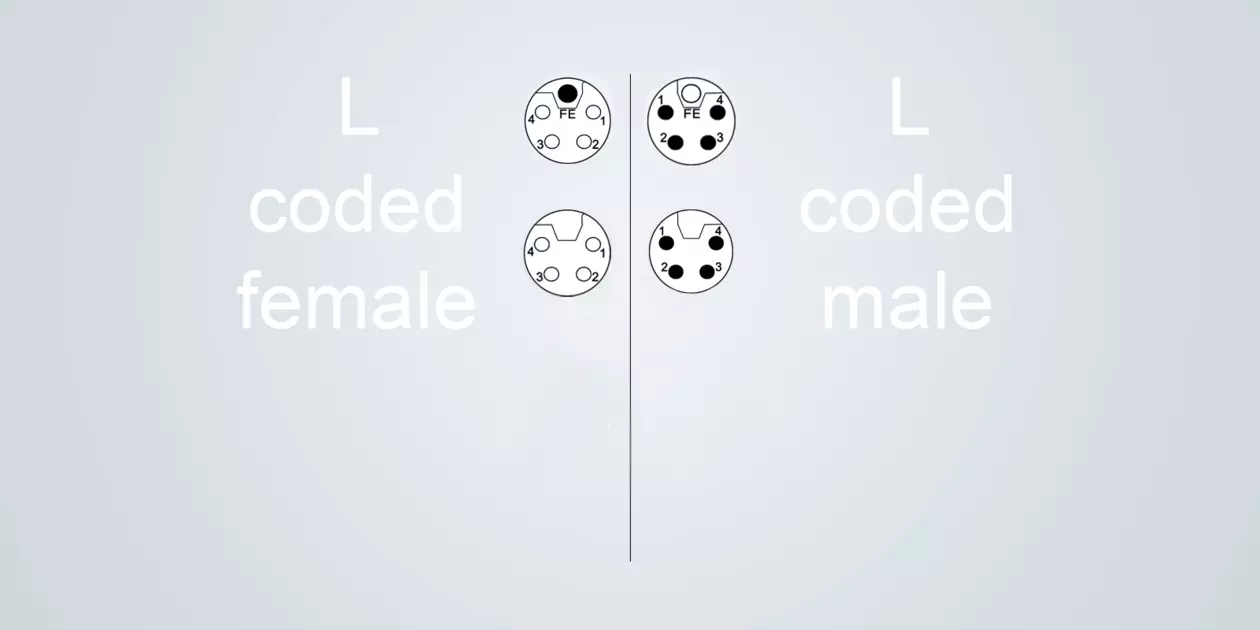
Typical application: Transmission of high currents and voltages
Size M12 (IEC 61076-2-111)
4 poles + FE
Rated current up to 16 A / 63 V
The L-coding is used for supplying power to devices. Compared to K-coding, it has a FE contact and is designed for a different voltage range.
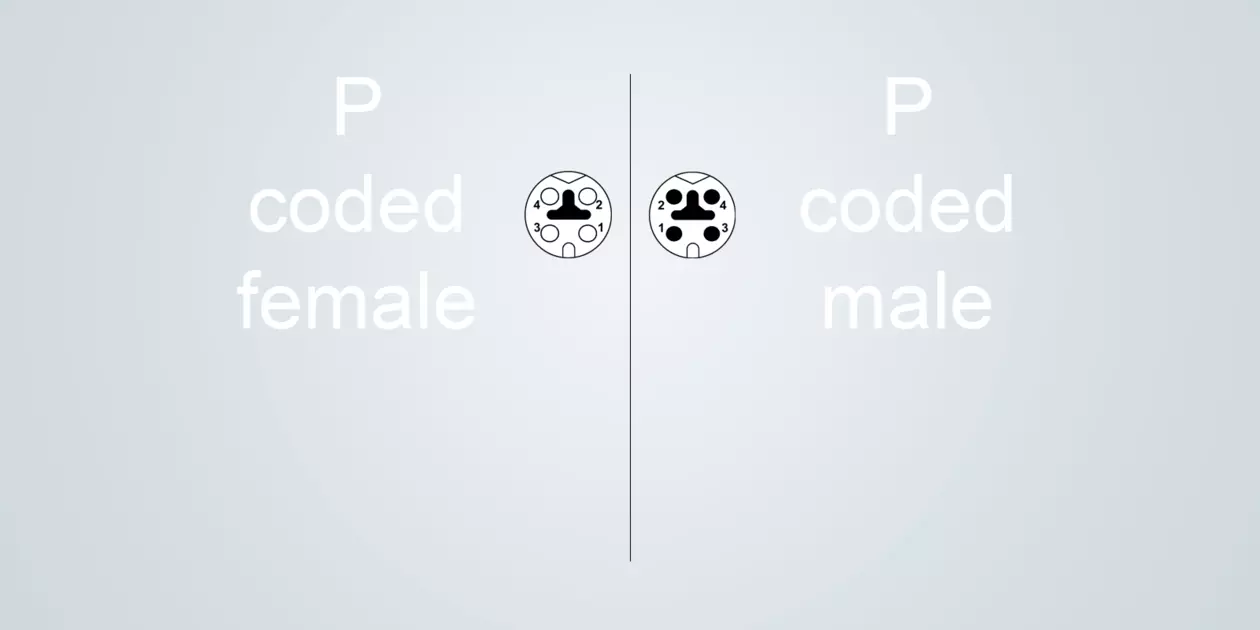
P-coded
Typical applications: Data & power transmission for EtherCAT P applications
Size M8 (IEC 61076-2-114)
4 poles
Rated current: 4 A / 60 V
100 Mbit/s
The P-coding is used for transmitting data in EtherCAT P protocols. It manages to simultaneously supply data and voltages up to 240 W.
S-coded
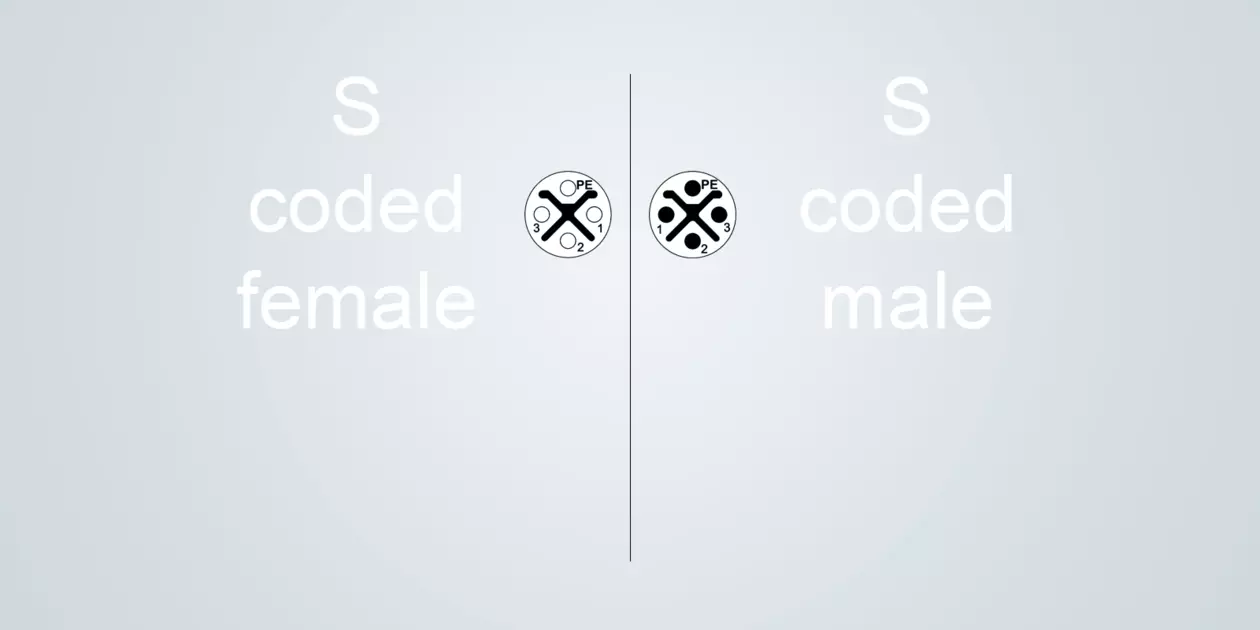
Typical application: Power connector for smaller devices
Size M12 (IEC 61076-2-111)
3 poles + PE
Electricity / voltage 12 A / 630 V
The S-coding is preferred for supplying power to smaller devices.
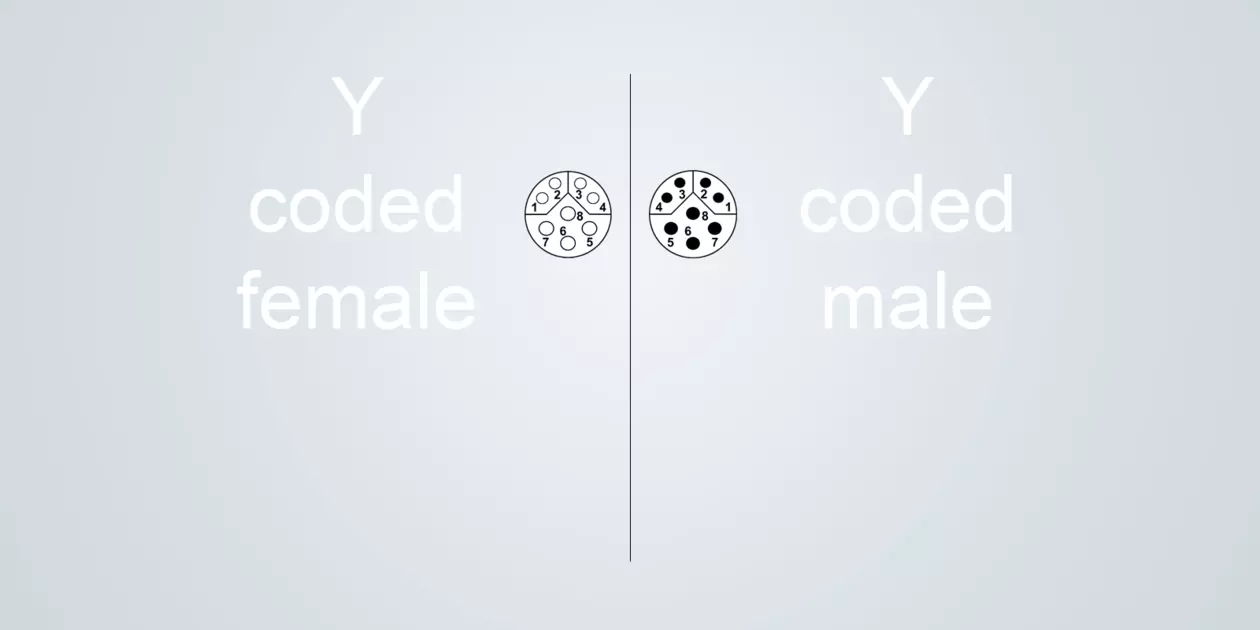
Y-coded
Typical application: Hybrid transmission of signals and power in one connector
Size M12 (IEC 61076-2-113)
8 poles (Type 4)
4 x power: 6 A, 50 V
4 x data: Kat. 5, 0.5 A, 50 V
Y-coding has a hybrid mating face. It simultaneously supplies devices with both essential lifelines of power and data. The four data contacts enable transmission rates of up to 100 Mbit/s Fast Ethernet. The four power contacts transmit power of up to 300 W. Hybrid connections, such as Y-coding, can simultaneous supply multiple lifelines. This avoids using separate interfaces, saves resources and actively supports the miniaturisation of devices.
X-coded
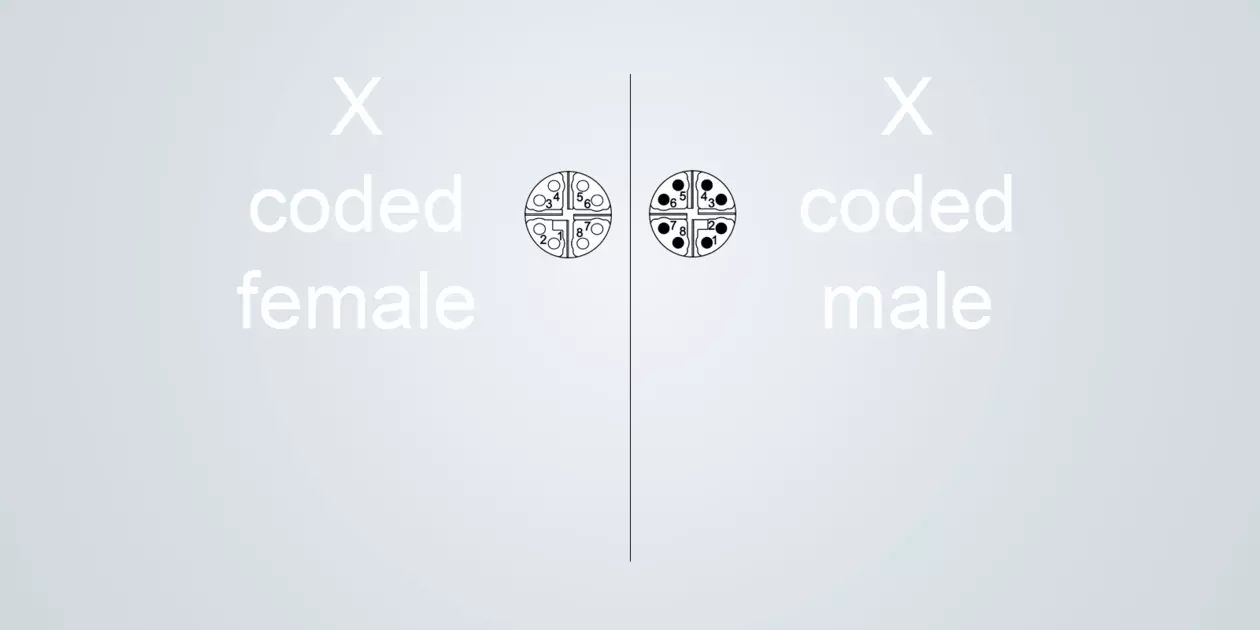
Typical application: Data interface for Industrial Ethernet networks
Size M12 (IEC 61076-2-109)
Data rate 1; 2.5; 10 Gbit/s
8 poles
X-coding is used for transmitting Industrial Ethernet in demanding environments. With its excellent shielding, this coding enables transmission rates of up to 10 Gbit/s. Data streams are well protected from electromagnetic influences by the robust metal housing.